Seals vs. Sea Lions: What’s the Difference?
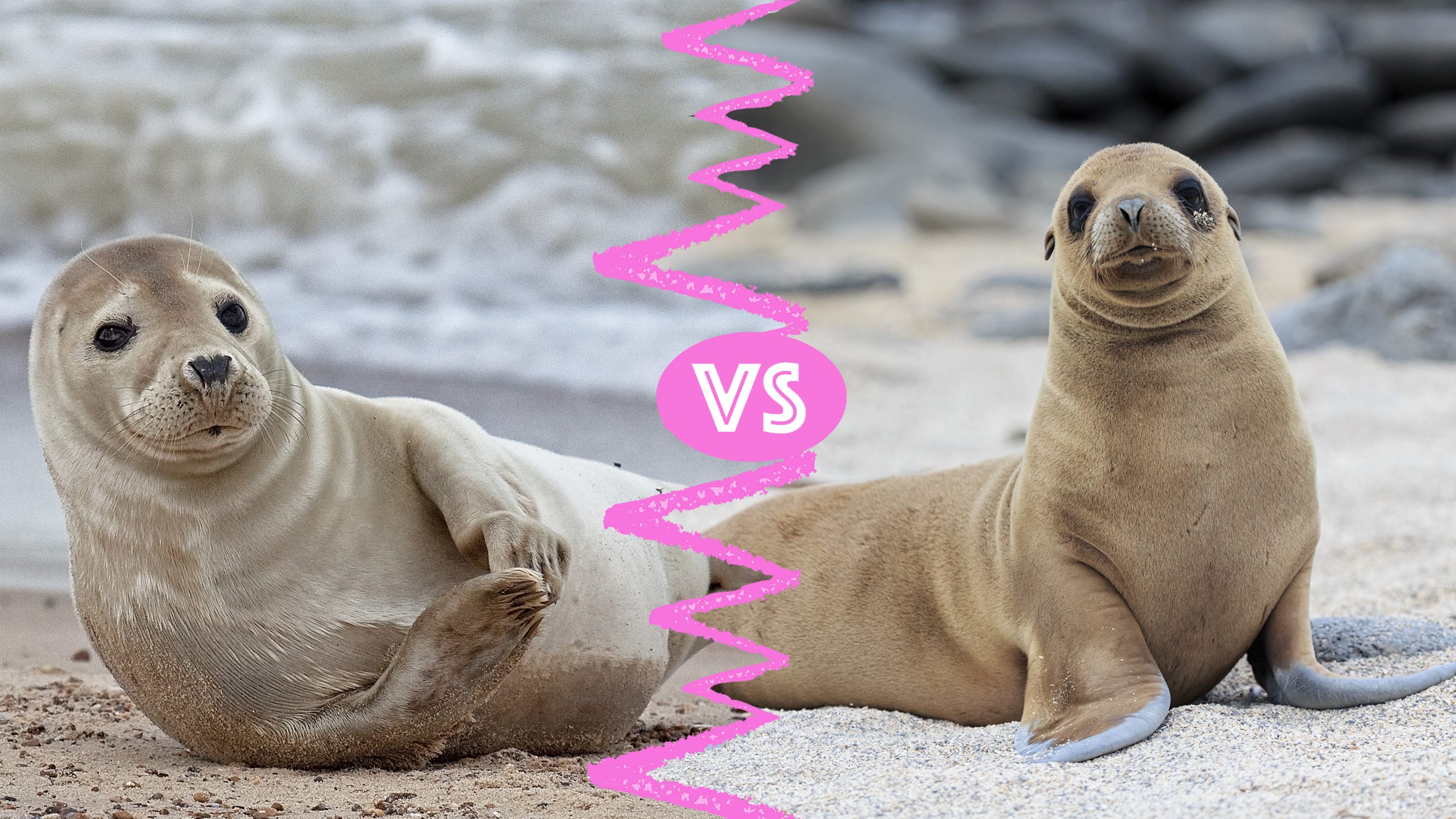
Ever been strolling along the coast, spotted a playful marine mammal, and found yourself completely stumped on whether it was a seal or a sea lion? You're not alone! These adorable animals share the same ocean habitat, but they have some key differences that set them apart.
It can be frustrating trying to tell these creatures apart, especially when you're trying to impress your friends or educate your kids. You might even feel a little foolish admitting you don't know the answer. The good news is, it's easier than you think to become a seal and sea lion expert!
This post is your ultimate guide to understanding the differences between seals and sea lions. We'll break down the key characteristics that distinguish these fascinating animals, from their flippers to their ears to their behavior. By the end of this read, you'll be able to confidently identify them like a pro!
In essence, we'll explore their physical characteristics, like ear flaps and flipper structure, and their behavior, such as how they move on land. We'll also touch upon their habitats and some fun facts to make learning about seals and sea lions engaging. Key terms to keep in mind are "ear flaps," "flipper locomotion," "social behavior," and "habitat differences." By understanding these core distinctions, you'll be well-equipped to tell these marvelous marine mammals apart.
Ear Flaps: The Most Obvious Difference
My first encounter with a sea lion was at Pier 39 in San Francisco. The noise was incredible – a cacophony of barks and honks that echoed across the water. I remember thinking, "Wow, those seals are loud!" It wasn't until a park ranger pointed out their visible ear flaps that I realized my mistake. These external ear flaps are one of the easiest ways to distinguish a sea lion from a seal. Seals, on the other hand, have small ear holes, but no external flaps. It was a lightbulb moment, and since then, I've never forgotten this crucial difference.
Let's delve deeper. The presence or absence of external ear flaps is the single most straightforward way to tell these animals apart. Sea lionshavethem; sealsdon't. This simple distinction can save you from embarrassing misidentifications and allows you to impress your friends with your newfound knowledge. Beyond the visual difference, the presence of ear flaps also influences how these animals hear. Sea lions have better hearing above water due to their external ears, while seals are more adapted for underwater hearing with their streamlined ear holes. So, the next time you see a marine mammal, take a close look at its ears – that's your first clue!
Flipper Locomotion: How They Move on Land
Seals and sea lions move quite differently on land, and this is another key distinguishing feature. Sea lions have large, powerful front flippers that they use to "walk" or rotate, and propel themselves forward, making them surprisingly agile on land. Think of them as little waddlers with a purpose! Seals, particularly harbor seals, tend to "scoot" or "hunch" along on their bellies, using their front flippers for minimal assistance and their hind flippers drag behind them. This makes them much less mobile on land than their sea lion cousins. This difference in locomotion is due to their skeletal structure and how their flippers are attached to their bodies.
The structure of their flippers and pelvic bones plays a huge role in their mobility. Sea lions have a more flexible pelvic girdle, allowing them to rotate their hind flippers forward and use them for walking. Seals, with their less flexible pelvic bones, are more limited in their hind flipper movement, resulting in the scooting motion. This difference in locomotion reflects the different lifestyles of these animals. Sea lions often haul out on land for extended periods, needing the ability to move around easily, while seals tend to spend more time in the water and only come ashore for resting and breeding. So, observing how they move on land is another valuable clue for identification.
History and Myth of Seals and Sea Lions
Throughout history, seals and sea lions have held different symbolic meanings in various cultures. In some indigenous coastal communities, seals are revered as providers of food, clothing, and oil, and are often featured in traditional stories and art. Sea lions, with their boisterous nature and large size, might be associated with strength, power, or even mischief. In mythology, seals have sometimes been depicted as creatures that can transform into humans, blurring the lines between the animal and human worlds. These cultural associations have shaped how we perceive and interact with these animals today.
The historical significance of seals and sea lions extends beyond mythology. For centuries, they were hunted for their fur, blubber, and meat, leading to significant population declines in some areas. This history of exploitation has prompted conservation efforts to protect these animals and their habitats. Today, seals and sea lions are often seen as symbols of marine conservation, highlighting the importance of protecting our oceans and the creatures that call them home. Understanding the history of human interaction with these animals can provide valuable insights into the challenges they face and the importance of ongoing conservation efforts. Therefore, knowing about the hunting background of the seals can help in the future.
Hidden Secrets: Social Behavior and Communication
Beyond their physical differences, seals and sea lions also differ in their social behavior and communication. Sea lions are known for their boisterous and social nature, often gathering in large groups on land and communicating through loud barks and honks. Seals, while still social, tend to be quieter and less demonstrative, often forming smaller groups and communicating through softer vocalizations. Their social structures also differ, with sea lions often exhibiting more complex social hierarchies than seals.
The differences in social behavior and communication reflect the different ecological niches occupied by these animals. Sea lions, with their larger size and more active lifestyle, benefit from living in large groups for protection and social interaction. Seals, with their more solitary nature, may be better adapted for foraging in specific habitats or avoiding competition with other seals. Understanding these differences in social behavior and communication can provide valuable insights into the complex lives of these fascinating marine mammals. Ultimately, observing the social interactions can explain a lot more about their species.
Recommendations: Where to See Them in the Wild
If you're eager to put your newfound knowledge to the test, there are many fantastic places to see seals and sea lions in the wild. In California, Pier 39 in San Francisco is famous for its colony of California sea lions, while Año Nuevo State Park is a great place to observe elephant seals during their breeding season. On the East Coast, you can often spot harbor seals along the coast of Maine and Massachusetts. When observing these animals, remember to keep a safe distance and avoid disturbing them, respecting their natural habitat. Remember to check what season it is before planning your trip!
Visiting these locations offers a unique opportunity to observe seals and sea lions in their natural environment and appreciate their beauty and behavior firsthand. Seeing them up close can also reinforce your understanding of the key differences between these animals and make you a more informed and engaged observer. Remember to bring your binoculars and a camera to capture the experience, and be prepared to be amazed by these incredible marine mammals. By observing seals and sea lions in their natural habitats, you are contributing to their preservation.
Diving Deeper: Diet and Feeding Habits
The diet and feeding habits of seals and sea lions are also essential to understanding their differences. Both are carnivores, but their specific prey and foraging strategies can vary. Sea lions tend to be more opportunistic feeders, consuming a wide range of fish, squid, and crustaceans. Seals, on the other hand, may have more specialized diets, focusing on specific types of fish or invertebrates. Their teeth and skull morphology reflect these dietary differences, with sea lions having sharper teeth for tearing flesh and seals having more robust jaws for crushing shellfish. Thus, diet dictates their feeding habitats.
Their diving abilities also play a crucial role in their foraging success. Both seals and sea lions are excellent divers, but their diving depths and durations can vary depending on their species and prey. Some seals, like the Weddell seal, can dive to incredible depths and hold their breath for over an hour, allowing them to access deep-sea prey. Sea lions, while not typically diving as deep as some seals, are still capable of impressive dives to catch their meals. Understanding their diet and feeding habits can provide valuable insights into their ecological roles and the challenges they face in a changing ocean environment. Studying their digestive system can also provide insights into their eating habits.
Tips for Identification: Beyond the Basics
While ear flaps and flipper locomotion are great starting points, there are other subtle clues that can help you distinguish between seals and sea lions. Pay attention to their size and shape. Sea lions tend to be larger and bulkier than seals, with more muscular necks and shoulders. Seals often have a more streamlined and elongated body shape. Also, observe their behavior in the water. Sea lions are generally more active and playful, often seen porpoising and interacting with each other, while seals tend to be more solitary and spend more time resting at the surface.
Furthermore, consider their geographic location. Different species of seals and sea lions inhabit different regions of the world, so knowing which species are likely to be found in a particular area can help narrow down your identification. Finally, don't be afraid to consult field guides or online resources to confirm your identification. With a little practice and attention to detail, you'll become a seal and sea lion identification expert in no time! Remembering the location that you are in can determine their species. By understanding, you are well on your way to becoming an expert.
Vocalizations: Listen Closely!
As mentioned earlier, the vocalizations of seals and sea lions differ significantly. Sea lions are known for their loud barks and honks, which they use for communication within their large social groups. These vocalizations can be heard from quite a distance, especially in areas with high sea lion densities. Seals, on the other hand, tend to be quieter, producing softer vocalizations such as grunts, hisses, and trills. Their vocalizations are often used for communication between mothers and pups or for maintaining social bonds within smaller groups. By listening closely to their vocalizations, you can gain another clue to help you distinguish between seals and sea lions.
These differences in vocalizations reflect their different social structures and communication needs. Sea lions, living in large and noisy groups, need loud and distinctive vocalizations to communicate effectively. Seals, with their smaller groups and more solitary habits, can rely on softer and more subtle vocalizations. The study of animal vocalizations, known as bioacoustics, is a fascinating field that can provide valuable insights into the behavior and ecology of marine mammals. Therefore, understanding how their vocal cords operate can help identify them.
Fun Facts: Amazing Adaptations
Seals and sea lions are full of surprises! Did you know that some seals can hold their breath for over an hour? Or that sea lions can swim at speeds of up to 25 miles per hour? These incredible adaptations allow them to thrive in a challenging marine environment. Seals have thick layers of blubber to insulate them from the cold, while sea lions have streamlined bodies and powerful flippers for efficient swimming. They also have specialized eyes that allow them to see clearly both above and below water. These amazing adaptations are a testament to the power of evolution and the resilience of these incredible creatures.
Besides, seals have whiskers, called vibrissae, that they use to detect prey in murky water. These whiskers are incredibly sensitive and can detect subtle vibrations in the water, allowing seals to locate fish even in complete darkness. Sea lions, with their social nature, have developed complex communication systems, using a variety of vocalizations and body postures to convey information to each other. Learning about these fun facts can deepen your appreciation for these amazing animals and inspire you to learn more about the natural world. Learning about these fun facts are very interesting and can help to become an expert.
How to Help: Conservation Efforts
Seals and sea lions face a variety of threats, including habitat loss, pollution, entanglement in fishing gear, and climate change. Fortunately, there are many things we can do to help protect these animals and their habitats. Supporting organizations that work to protect marine mammals, reducing our use of plastic, and advocating for policies that protect our oceans are all important steps. You can also educate yourself and others about the challenges facing seals and sea lions and inspire others to take action. By working together, we can ensure that these amazing animals continue to thrive for generations to come.
In addition to these actions, you can also make conscious choices in your daily life to reduce your impact on the environment. For example, you can choose to eat sustainably sourced seafood, reduce your carbon footprint by using public transportation or biking, and support businesses that are committed to environmental sustainability. Every little bit helps, and by working together, we can make a big difference for seals, sea lions, and all marine life. Thus, helping them is important for conservation efforts. Doing this can help with the current state of the animal, such as seals and sea lions.
What If: Future Threats and Challenges
The future of seals and sea lions is uncertain, as they face increasing threats from climate change, pollution, and human activities. As ocean temperatures rise, their prey may become less available, forcing them to travel further to find food. Pollution, especially plastic pollution, can entangle and harm these animals. Human activities, such as coastal development and oil exploration, can destroy their habitats and disrupt their breeding patterns. If we don't take action to address these threats, we risk losing these amazing animals forever. The biggest action that can be taken is to not litter and take responsibility.
It's crucial that we continue to monitor seal and sea lion populations and implement conservation measures to mitigate these threats. This includes protecting their habitats, reducing pollution, and addressing climate change. We also need to work with local communities to promote sustainable fishing practices and reduce human-wildlife conflict. By taking proactive measures, we can help ensure that seals and sea lions have a future in our oceans. It's our responsibility to protect these animals and the ecosystems they depend on. Thus, we must protect them for many years to come. It is an advantage for our world.
Listicle: Top 5 Differences Between Seals and Sea Lions
Here's a quick recap of the top 5 differences between seals and sea lions:
- Ear Flaps: Sea lions have visible ear flaps; seals do not.
- Flipper Locomotion: Sea lions can rotate their hind flippers forward and "walk" on land; seals scoot or hunch along.
- Size and Shape: Sea lions tend to be larger and bulkier than seals.
- Vocalization: Sea lions are loud and bark; seals are quieter and produce softer vocalizations.
- Social Behavior: Sea lions are highly social and gather in large groups; seals are more solitary.
Keep these key differences in mind, and you'll be able to confidently identify seals and sea lions wherever you encounter them! This listicle should help with identifying the differences. Therefore, we can differentiate their species from one another. With the listicle, there will be no confusion.
Question and Answer
Q: What is the easiest way to tell a seal and sea lion apart?
A: Look for ear flaps! Sea lions have them, seals don't.
Q: How do seals and sea lions move on land?
A: Sea lions "walk" using their front and hind flippers, while seals scoot on their bellies.
Q: Are sea lions louder than seals?
A: Yes, sea lions are known for their loud barks and honks, while seals are generally quieter.
Q: Where can I see seals and sea lions in the wild?
A: Pier 39 in San Francisco is famous for sea lions, and Año Nuevo State Park is a great place to see elephant seals. You can also spot harbor seals along the coasts of Maine and Massachusetts.
Conclusion of Seals vs. Sea Lions: What’s the Difference?
With these newfound knowledge and tips and tricks, it's now time to apply this. Identifying species can be hard, but with some help, it gets easier and easier. So go on and tell your friends this tips and trick. Show them that you are the next expert of marine animals.
0 Response to "Seals vs. Sea Lions: What’s the Difference?"
Post a Comment