How Animals Adapt to Extreme Weather
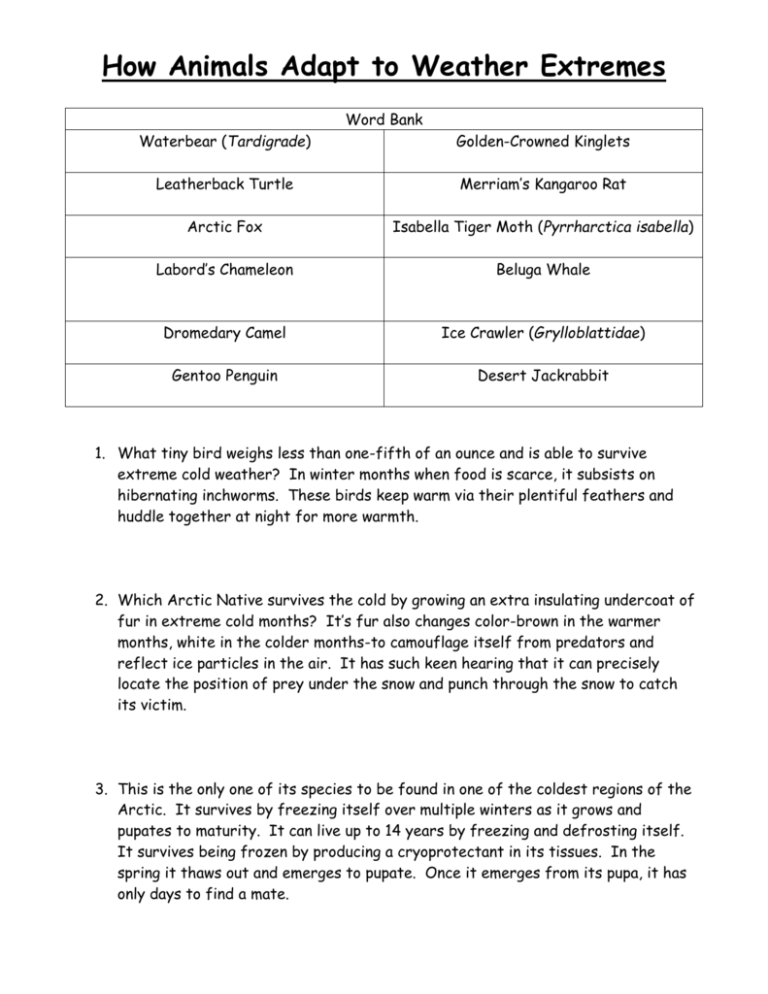
Have you ever wondered how animals survive scorching deserts or freezing arctic tundras? It's more than just luck; it's a testament to the incredible power of adaptation. From the smallest insect to the largest mammal, life finds a way to not only persist but thrive in the face of challenging conditions.
The increasing frequency and intensity of extreme weather events are putting immense pressure on ecosystems around the globe. Animals are facing unprecedented challenges in finding food, maintaining their body temperature, and even simply surviving catastrophic events like floods and wildfires. This raises concerns about the long-term health and stability of animal populations and the delicate balance of nature.
Animals adapt to extreme weather conditions through a remarkable array of physical, physiological, and behavioral changes. These adaptations can be inherited, learned, or a combination of both. They allow animals to cope with extreme temperatures, lack of water, intense sunlight, and other environmental stressors, ensuring their survival and the continuation of their species. We're talking about evolution in action, right before our eyes!
In summary, animals have developed fascinating adaptations to endure extreme weather. These include physical changes like thick fur or specialized kidneys, physiological processes such as hibernation or estivation, and behavioral strategies like migration or seeking shelter. Keywords to remember are adaptation, extreme weather, survival, physical adaptations, physiological adaptations, and behavioral adaptations. These adaptations are crucial for animal survival in a world increasingly impacted by climate change.
The Wonders of Hibernation
Hibernation is one of the most incredible examples of animal adaptation to extreme cold. I remember reading about bears hibernating in caves during the winter, and it always seemed like something out of a fairy tale. It's a period of inactivity characterized by a significant decrease in body temperature, metabolic rate, and heart rate. Animals like groundhogs, bats, and certain species of squirrels enter a state of torpor, where they conserve energy and survive on stored fat reserves. This remarkable adaptation allows them to weather the harsh winter months when food is scarce and temperatures plummet. Hibernation isn't just about sleeping; it's a complex physiological process that requires careful preparation and precise regulation. The ability to drastically slow down their metabolism allows these animals to survive for months without eating, drinking, or even urinating. It’s a true testament to the resilience of life.
Migration: A Journey for Survival
Migration is a long-distance movement of animals from one region to another, often in response to seasonal changes in weather or food availability. Many birds, mammals, and insects undertake incredible journeys, sometimes spanning thousands of miles, to find more favorable conditions. For example, monarch butterflies migrate from Canada and the United States to Mexico each year to escape the cold winter months. Similarly, many species of birds fly south for the winter to find warmer temperatures and a more abundant food supply. Migration is a risky endeavor, as animals face numerous challenges along the way, including predators, starvation, and exhaustion. However, the benefits of reaching a more suitable environment often outweigh the risks. Migration patterns are often ingrained behaviors passed down through generations. Navigation is often guided by the sun, stars, or Earth's magnetic field.
Estivation: The Summer Sleep
While hibernation is a well-known adaptation to cold weather, estivation is its less famous cousin. It is a period of dormancy that occurs during hot, dry periods. Animals that estivate, such as some amphibians, reptiles, and insects, enter a state of inactivity to conserve energy and avoid the harsh conditions of summer. During estivation, their metabolic rate slows down, and they may burrow underground or find a cool, moist place to wait out the heat. Estivation is similar to hibernation in that it allows animals to survive periods of environmental stress, but it is triggered by different environmental cues. Some animals, like the lungfish, can survive for months or even years in a state of estivation, encased in a cocoon of mud. This remarkable adaptation allows them to survive in environments where water is scarce and temperatures are extreme.
Camouflage: Blending In
Camouflage is a physical adaptation that allows animals to blend in with their surroundings, providing protection from predators or allowing them to ambush prey. Many animals have evolved coloration, patterns, and shapes that mimic their environment, making them difficult to spot. For example, the Arctic fox has a white coat in the winter to blend in with the snow, while the chameleon can change its skin color to match its surroundings. Camouflage is an effective strategy for survival in environments where predators are common or where prey is difficult to find. It allows animals to avoid detection and increase their chances of survival. Camouflage can be passive, where an animal's appearance naturally blends in with its environment, or active, where an animal can change its appearance to match its surroundings.
The Role of Fat Storage
Fat storage is a crucial adaptation for animals living in environments with seasonal food shortages. Animals like bears, squirrels, and marmots accumulate large reserves of fat during periods of abundance, which they then use as an energy source during times of scarcity. Fat is an excellent source of energy, as it provides more than twice the calories per gram as carbohydrates or proteins. Storing fat allows animals to survive for extended periods without eating, which is essential during hibernation or migration. The amount of fat that an animal needs to store depends on the length and severity of the food shortage. Some animals, like the polar bear, can accumulate massive amounts of fat to survive the harsh Arctic winter. The ability to store fat is a key adaptation that allows animals to thrive in environments with fluctuating food availability.
Seeking Shelter: Protection from the Elements
Seeking shelter is a behavioral adaptation that allows animals to protect themselves from extreme weather conditions, predators, and other environmental hazards. Many animals build nests, burrows, or dens to provide a safe and comfortable place to rest and raise their young. Birds build nests in trees or bushes to protect their eggs and chicks from the elements and predators. Mammals dig burrows in the ground to escape the heat of the sun or the cold of winter. Some animals, like the hermit crab, use shells as portable shelters. Seeking shelter is a simple but effective way for animals to improve their chances of survival in a challenging environment. The type of shelter that an animal seeks depends on its size, habitat, and the specific threats that it faces.
Diurnal vs. Nocturnal Behavior
Diurnal and nocturnal behaviors represent fascinating adaptations to different environmental conditions. Diurnal animals, like humans and squirrels, are active during the day, while nocturnal animals, like bats and owls, are active at night. This difference in activity patterns is often driven by factors such as temperature, predation risk, and food availability. In hot environments, nocturnal behavior can help animals avoid the scorching sun and conserve water. In environments with high predation risk, nocturnal behavior can help animals avoid being seen by predators. Diurnal and nocturnal behaviors are often accompanied by specialized sensory adaptations. For example, nocturnal animals often have excellent night vision and hearing, while diurnal animals often have good color vision.
Fun Facts About Animal Adaptations
Did you know that the camel can survive for weeks without water? This is due to a number of adaptations, including its ability to tolerate dehydration, its efficient kidneys, and its ability to store water in its bloodstream. Or that the emperor penguin can withstand temperatures as low as -40 degrees Celsius? This is thanks to its thick layer of feathers and fat, as well as its ability to huddle together with other penguins to conserve heat. These are just a few examples of the incredible adaptations that animals have evolved to survive in extreme environments. The more we learn about these adaptations, the more we appreciate the diversity and resilience of life on Earth. Animal adaptations are often surprising and unexpected, reflecting the diverse challenges that animals face in their environments.
How Humans Can Help Animals Adapt
While animals are remarkably adaptable, they are facing unprecedented challenges due to climate change and habitat loss. Humans can play a crucial role in helping animals adapt to these changing conditions by reducing our carbon footprint, protecting and restoring habitats, and supporting conservation efforts. By reducing our greenhouse gas emissions, we can slow down the rate of climate change and give animals more time to adapt. By protecting and restoring habitats, we can provide animals with the resources and space they need to survive. And by supporting conservation efforts, we can help scientists and conservationists learn more about animal adaptations and develop strategies to protect them. Our actions can make a real difference in the lives of animals and the health of our planet.
What If Animals Couldn't Adapt?
The consequences of animals being unable to adapt to extreme weather would be catastrophic. Ecosystems would collapse, food webs would unravel, and biodiversity would plummet. Many species would face extinction, leading to a significant loss of genetic diversity and ecosystem services. The loss of pollinators, seed dispersers, and other keystone species would have cascading effects on the environment. The impact would not only be felt by animals but also by humans, who rely on healthy ecosystems for food, water, and other essential resources. The ability of animals to adapt is crucial for the health and stability of our planet. It's a reminder of the interconnectedness of all living things and the importance of protecting biodiversity.
Listicle: 5 Amazing Animal Adaptations
Here's a quick list of some truly remarkable animal adaptations: 1. The Arctic Fox's Winter Coat: Turning pure white to blend seamlessly with the snowy landscape.
2. The Camel's Water-Saving Abilities: Surviving weeks in the desert without drinking.
3. The Emperor Penguin's Huddling Behavior: Sharing warmth to withstand freezing temperatures.
4. The Monarch Butterfly's Epic Migration: Flying thousands of miles to warmer climates.
5. The Wood Frog's Freezing Tolerance: Surviving being frozen solid during winter. These adaptations highlight the incredible diversity and ingenuity of life on Earth.
Question and Answer About How Animals Adapt to Extreme Weather
Q: What is the most common adaptation animals use to survive extreme cold?
A: Hibernation is a widespread strategy, allowing animals to conserve energy and survive on stored fat reserves.
Q: How do animals adapt to extreme heat?
A: Many animals become nocturnal to avoid the heat of the day, while others estivate or use evaporative cooling mechanisms like sweating or panting.
Q: What role does camouflage play in animal survival?
A: Camouflage helps animals blend in with their surroundings, providing protection from predators or allowing them to ambush prey.
Q: Can humans help animals adapt to extreme weather?
A: Yes! By reducing our carbon footprint, protecting habitats, and supporting conservation efforts, we can make a significant difference.
Conclusion of How Animals Adapt to Extreme Weather
The natural world is full of inspiring examples of animals finding solutions to thrive in the face of difficult environmental conditions. By understanding the different ways that animals adapt to extreme weather, we can better appreciate the resilience of life and the importance of protecting biodiversity. As climate change continues to pose new challenges, it is crucial that we support animal conservation efforts and work to mitigate the impacts of extreme weather on our planet.
0 Response to "How Animals Adapt to Extreme Weather"
Post a Comment