The Life Cycle of a Frog
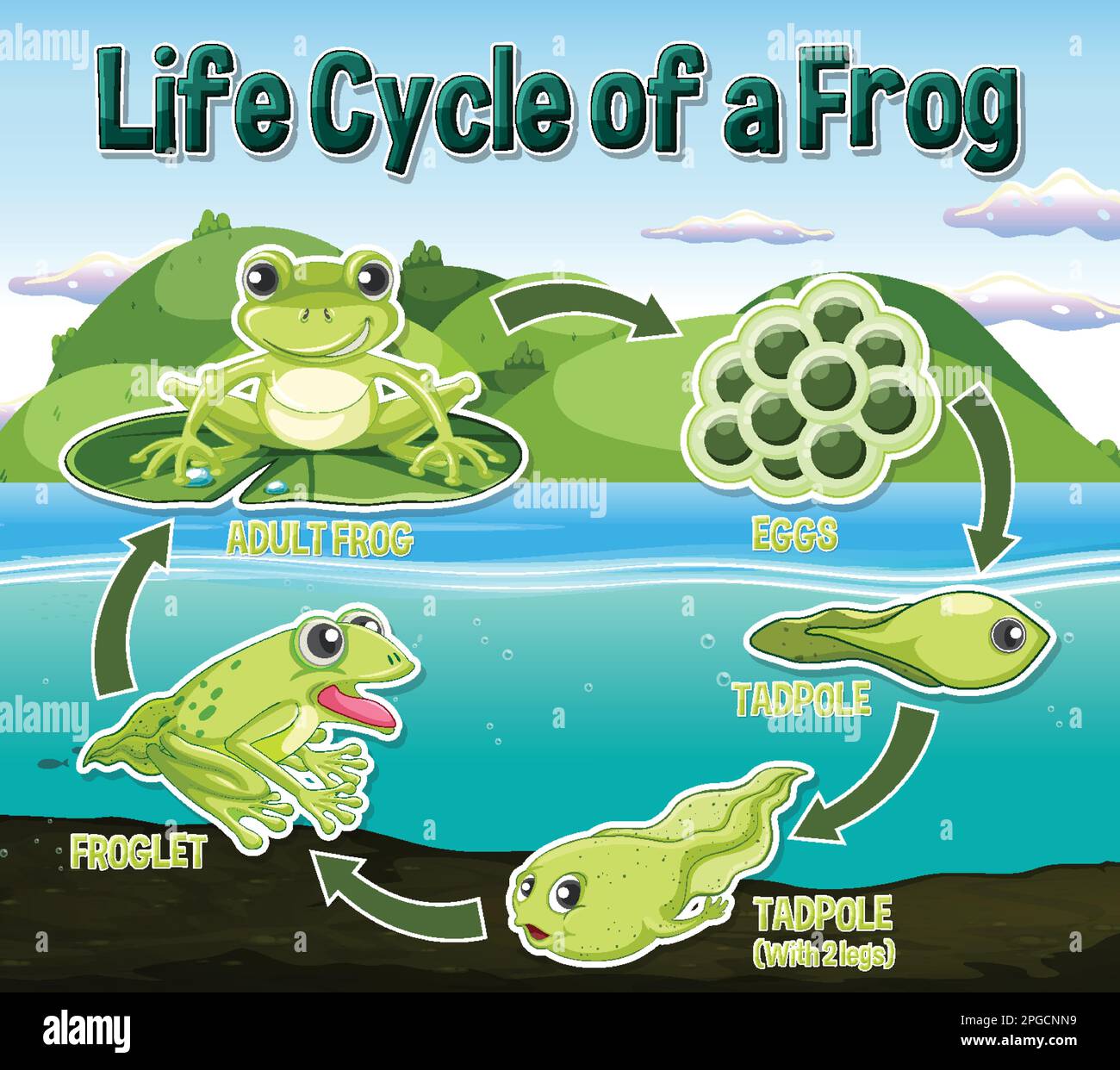
Have you ever stopped to consider the incredible journey a tiny frog takes from a humble egg to a hopping adult? It's a transformation so profound, it rivals any superhero origin story. Get ready to dive into the fascinating world of amphibian development!
Understanding the stages a frog goes through can sometimes feel overwhelming. There are so many changes happening, and it's easy to get lost in the details. Plus, grasping the environmental factors that influence this process can be tricky. What happens when their pond dries up? Or when pollution threatens their fragile existence? It's a lot to consider!
This post is for anyone curious about nature's wonders, especially those interested in the remarkable development of frogs. Whether you're a student, a teacher, or simply a nature enthusiast, you'll find something to spark your interest here. We'll explore each stage of the frog's life cycle, from egg to tadpole to froglet to adult, unraveling the mysteries of this incredible transformation.
This article explores the fascinating life cycle of a frog, covering each stage from egg to adult, highlighting key transformations and environmental influences. We delve into the processes of metamorphosis, limb development, and adaptation, revealing the wonders of amphibian life. Keywords include: frog life cycle, tadpole, metamorphosis, amphibian development, froglet, frog eggs.
Frog Eggs: The Beginning
The journey begins with the frog egg, often laid in masses or clusters in water. My own first encounter with frog eggs was during a childhood trip to a local pond. I remember being mesmerized by the gelatinous blobs clinging to submerged plants, each one holding the promise of a new life. It was like discovering a secret world, hidden beneath the surface of the water. These eggs are vulnerable, relying on the surrounding aquatic environment for protection and nourishment. A single female frog can lay hundreds, even thousands, of eggs at a time, increasing the chances that some will survive. The eggs are typically dark on top and light on the bottom, providing camouflage against predators from above and below. The jelly-like substance surrounding the eggs not only protects them but also helps maintain moisture and provides a source of initial nutrients for the developing embryos. This stage is highly susceptible to environmental changes, like temperature fluctuations and pollution, making clean and stable water conditions crucial for successful hatching. Frog eggs represent the hopeful beginning of a complex and wondrous life cycle, a testament to nature's resilience and adaptability. Even minor changes in their environment can significantly impact their survival rate. The egg stage emphasizes the delicate balance within ecosystems and the interconnectedness of life.
The Tadpole Stage: Life Aquatic
The tadpole emerges from the egg, a creature entirely different from the adult frog it will become. Imagine a small, swimming fish with a long tail and gills for breathing underwater. This is the tadpole, an herbivore that feeds on algae and plant matter. This stage is all about growth and development. Tadpoles have a relatively simple body plan, focused on acquiring energy and preparing for the dramatic metamorphosis to come. They swim using their tail, which propels them through the water as they graze on vegetation. Internally, the tadpole is developing the organs and structures that will be essential for its future life on land. Lungs are forming, limbs are budding, and the digestive system is adapting to a more carnivorous diet. The length of the tadpole stage varies depending on the species and environmental conditions. Some tadpoles transform into froglets in a matter of weeks, while others may remain in the tadpole stage for months or even years. This variability highlights the adaptability of frogs to different environments. Predation is a significant threat to tadpoles, with fish, birds, and other aquatic animals preying on them. Tadpoles use various strategies to avoid predators, including camouflage, schooling behavior, and rapid swimming. The tadpole stage is a critical period of development, setting the stage for the frog's eventual transition to a terrestrial lifestyle.
Metamorphosis: The Great Transformation
Metamorphosis is perhaps the most remarkable part of the frog's life cycle, a complete transformation from an aquatic tadpole to a terrestrial frog. For centuries, cultures around the world have been fascinated by this dramatic change, often associating it with themes of rebirth, transformation, and the cyclical nature of life. In ancient Egypt, the frog was a symbol of fertility and regeneration, linked to the annual flooding of the Nile. The Greeks and Romans also associated frogs with water and the renewal of life. In many indigenous cultures, frogs are seen as powerful spiritual beings, capable of bridging the gap between the physical and spiritual worlds. Some myths depict frogs as guardians of water sources or as messengers from the gods. The frog's ability to transform from a tadpole to a frog is often interpreted as a metaphor for personal growth and change. It represents the potential for individuals to overcome obstacles and achieve their full potential. In some cultures, the frog is also associated with good luck and prosperity. Carrying a frog charm or having a frog image in the home is believed to bring good fortune. The rich history and mythology surrounding frogs reflect the deep connection between humans and these fascinating amphibians. Their unique life cycle has captivated our imaginations for centuries, inspiring stories, art, and spiritual beliefs.
Hidden Secrets: Inside the Frog
Delving deeper into the frog's biology reveals some fascinating hidden secrets. Did you know that some frogs can change color to blend in with their surroundings? Or that certain species have poisonous skin secretions that deter predators? These adaptations are crucial for survival in a diverse range of habitats. Frogs are ectothermic, meaning they rely on external sources of heat to regulate their body temperature. This is why you often see frogs basking in the sun or seeking shelter in cool, damp places. Their skin is highly permeable, allowing them to absorb water and oxygen directly from the environment. This also makes them particularly vulnerable to pollutants, as toxins can easily enter their bodies through their skin. Frogs play a vital role in many ecosystems, both as predators and prey. They consume insects and other invertebrates, helping to control populations and prevent outbreaks. In turn, they are a food source for birds, snakes, and other animals. Some frog species have developed unique reproductive strategies. For example, the Darwin's frog carries its tadpoles in its vocal sac, protecting them until they are ready to metamorphose. Other species lay their eggs in foam nests or on the backs of their mothers, providing extra care for their offspring. These hidden secrets highlight the complexity and diversity of frog biology, revealing the remarkable adaptations that allow them to thrive in a variety of environments.
Recommendations: Helping Frogs Thrive
Given the challenges frogs face, what can we do to help them thrive? Protecting their habitats is crucial. This means conserving wetlands, reducing pollution, and promoting sustainable land management practices. Creating frog-friendly gardens can also make a difference. By providing shelter, water sources, and native plants, you can create a welcoming habitat for frogs in your own backyard. Avoid using pesticides and herbicides, as these chemicals can be harmful to frogs and other wildlife. Educating others about the importance of frog conservation is also essential. Spread the word about the threats frogs face and encourage others to take action. Support organizations that are working to protect frog habitats and populations. By working together, we can make a difference in the lives of these amazing amphibians. Consider participating in citizen science projects, such as frog monitoring programs. These projects allow you to contribute valuable data on frog populations and distribution. Advocate for policies that protect wetlands and reduce pollution. By raising your voice, you can help ensure that frogs have a safe and healthy future. Every small action can make a difference in the fight to protect frogs and their habitats.
Adult Frog: Life on Land and Water
The adult frog is well-adapted to life on both land and water. With strong legs for jumping, webbed feet for swimming, and a long, sticky tongue for catching prey, the adult frog is a versatile predator. They primarily feed on insects, but some larger species may also eat small fish, rodents, and even other frogs. Adult frogs play an important role in controlling insect populations, helping to keep ecosystems in balance. They are also an important food source for other animals, such as snakes, birds, and mammals. Frogs use a variety of strategies to avoid predators, including camouflage, jumping, and poisonous skin secretions. Some species can even inflate their bodies to appear larger and more threatening. Reproduction typically occurs in water, with males attracting females through their calls. The calls vary depending on the species, ranging from simple croaks to complex songs. After mating, the female lays her eggs in the water, and the cycle begins anew. The adult frog stage is all about reproduction and ensuring the continuation of the species. They must find suitable mates, avoid predators, and secure a safe place to lay their eggs. The success of the adult frog stage depends on the health of the environment and the availability of resources. Habitat loss, pollution, and climate change all pose significant threats to frog populations. By protecting frog habitats and reducing pollution, we can help ensure that these amazing amphibians continue to thrive.
Tips for Spotting Frogs
Want to see frogs in the wild? Here are some tips for spotting these elusive creatures. The best time to look for frogs is during the evening or at night, when they are most active. Look for them near water sources, such as ponds, streams, and wetlands. Listen for their calls, which can help you locate them even if you can't see them. Be patient and move slowly, as frogs are easily startled. Wear dark clothing to blend in with your surroundings. Use a flashlight to scan the water's edge and vegetation. Look for frogs perched on rocks, logs, and leaves. Avoid disturbing their habitat or handling them unnecessarily. Bring a camera to capture your observations. With a little patience and observation, you'll be amazed at the diversity of frogs you can find in your local area. Remember to respect their environment and avoid causing any harm. By following these tips, you can increase your chances of spotting frogs and learning more about these fascinating amphibians. Consider joining a local frog monitoring group to help track populations and learn more about their behavior. Observe their behavior and take notes on their habitat, diet, and interactions with other species. By becoming a keen observer, you can contribute to our understanding of frog ecology and conservation.
Frog Habitats: Where Do They Live?
Frogs can be found in a wide variety of habitats, from tropical rainforests to deserts. Their distribution depends on factors such as temperature, rainfall, and the availability of water. Some frogs are highly specialized to specific habitats, while others are more adaptable. In tropical rainforests, frogs can be found in trees, on the ground, and in the water. They often have bright colors and patterns that help them blend in with the lush vegetation. In deserts, frogs have adapted to survive in arid conditions. They may burrow underground during the day to avoid the heat and emerge at night to hunt for food. Wetlands are particularly important habitats for frogs, providing breeding grounds and refuge from predators. Many frog species are dependent on wetlands for their survival. Urban areas can also provide habitat for frogs, although they face many challenges in these environments. Pollution, habitat fragmentation, and introduced species can all negatively impact frog populations in urban areas. By creating frog-friendly gardens and reducing pollution, we can help frogs thrive in our cities. Understanding the habitat requirements of different frog species is crucial for effective conservation efforts. Protecting and restoring frog habitats is essential for ensuring the survival of these amazing amphibians.
Fun Facts About Frogs
Frogs are full of surprises! Did you know that some frogs can jump over 20 times their body length? Or that the poison dart frog is one of the most toxic animals on Earth? Here are some more fun facts about frogs to amaze and entertain you. Some frogs can survive being frozen solid during the winter and thaw out in the spring. The wood frog is a master of this survival strategy. The Goliath frog is the largest frog in the world, reaching up to 1 foot in length and weighing over 7 pounds. The poison dart frog's bright colors serve as a warning to potential predators. Their skin contains potent toxins that can cause paralysis or death. Some frogs can change their sex in response to environmental conditions. This phenomenon is known as sequential hermaphroditism. Frogs have been around for over 200 million years, making them one of the oldest groups of amphibians. They have survived through numerous mass extinctions and continue to thrive in a variety of habitats. The study of frogs is called batrachology. Batrachologists study the biology, ecology, and conservation of frogs and other amphibians. These fun facts highlight the diversity and adaptability of frogs, showcasing their unique place in the animal kingdom.
How to Create a Frog-Friendly Garden
Creating a frog-friendly garden is a great way to support these amazing amphibians. Start by providing a water source, such as a pond or a shallow dish filled with water. Be sure to keep the water clean and free of chemicals. Provide shelter for frogs by planting native plants, creating rock piles, or adding logs to your garden. Avoid using pesticides and herbicides, as these chemicals can be harmful to frogs. Encourage a diversity of insects in your garden, as frogs rely on insects for food. Plant native flowers that attract pollinators. Remove invasive plants that can outcompete native vegetation. Provide a variety of microhabitats in your garden, such as sunny and shady areas, dry and moist areas. This will allow frogs to choose the conditions that best suit their needs. Avoid using artificial lighting, as this can disrupt frog behavior. Provide a safe passage for frogs to enter and exit your garden. This can be done by creating a ramp or a gentle slope leading to the water source. By creating a frog-friendly garden, you can provide a valuable habitat for these amazing amphibians.
What if Frogs Disappeared?
Imagine a world without frogs. What would be the consequences? The loss of frogs would have a significant impact on ecosystems, as they play a vital role in controlling insect populations and serving as a food source for other animals. Insect populations could explode, leading to crop damage and the spread of diseases. The populations of animals that prey on frogs, such as snakes and birds, could decline. The balance of ecosystems could be disrupted, leading to unforeseen consequences. The loss of frogs would also have economic impacts, as they are used in scientific research and as a food source in some cultures. The decline of frog populations is a warning sign of environmental degradation. It indicates that our ecosystems are under stress and that we need to take action to protect them. By conserving frog habitats and reducing pollution, we can help ensure that these amazing amphibians continue to thrive. The disappearance of frogs would be a tragic loss for biodiversity and a sign of environmental crisis. It is our responsibility to protect these amazing creatures and ensure their survival for future generations.
Top 5 Reasons to Love Frogs
Here's a list of reasons why frogs are so amazing:
- They are important indicators of environmental health.
- They play a vital role in controlling insect populations.
- They are a food source for other animals.
- They have unique adaptations that allow them to thrive in a variety of habitats.
- They are fascinating creatures that captivate our imaginations.
These are just a few of the many reasons to love frogs. They are an essential part of our ecosystems and deserve our protection. By learning more about frogs and their role in the environment, we can help ensure their survival for future generations.
Question and Answer about The Life Cycle of a Frog
Q1: How long does it take for a frog egg to hatch?
A1: The incubation period for frog eggs varies depending on the species and environmental conditions, but it typically ranges from a few days to several weeks.
Q2: What do tadpoles eat?
A2: Tadpoles are primarily herbivores, feeding on algae and plant matter in the water.
Q3: How long does it take for a tadpole to transform into a frog?
A3: The length of the tadpole stage varies depending on the species and environmental conditions, but it can range from a few weeks to several years.
Q4: What are some of the threats facing frog populations?
A4: Habitat loss, pollution, climate change, and introduced species are all major threats to frog populations.
Conclusion of The Life Cycle of a Frog
The life cycle of a frog is a testament to the wonders of nature. From the delicate egg to the hopping adult, each stage is a marvel of adaptation and transformation. By understanding and appreciating this incredible journey, we can better protect these vital members of our ecosystems and ensure their survival for generations to come. Let's all do our part to create a world where frogs can thrive!
0 Response to "The Life Cycle of a Frog"
Post a Comment